Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe and occur when the immune system overreacts to a specific substance. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to recognize and respond to an allergic reaction.
Types of Allergic Reactions
Mild Reactions
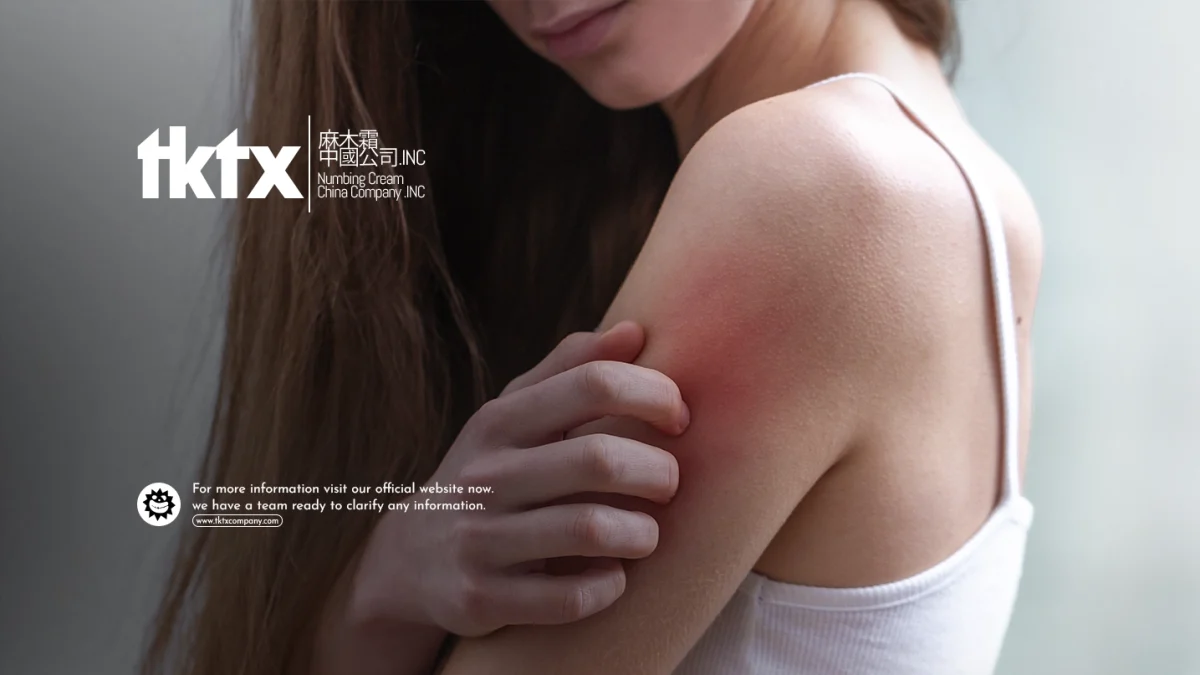
- Symptoms: Rashes, itching, watery eyes, nasal congestion, sneezing.
- Common Causes: Pollen, dust, pet dander, certain foods.
Moderate Reactions
- Symptoms: Hives, swelling, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Common Causes: Insect stings, foods, medications.
Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
- Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, throat swelling, low blood pressure, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- Common Causes: Bee stings, foods like peanuts and shellfish, medications.
Immediate Steps for Treating Allergic Reactions
Mild to Moderate Reactions
- Identify and Remove Allergen: If possible, identify and remove the source of the allergy.
- Take an Antihistamine: Medications like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help relieve mild to moderate symptoms.
- Wash Affected Area: If the reaction is on the skin, wash the area with water and mild soap to remove the allergen.
- Apply Cold Compresses: To alleviate itching and swelling, apply cold compresses to the affected area.
Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
- Administer Epinephrine: If the person has an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen), administer it immediately.
- Call Emergency Services: After administering epinephrine, call emergency services or go to the hospital immediately.
- Place the Person in Recovery Position: If the person is unconscious, place them on their side in the recovery position and monitor their breathing.
- Perform CPR if Necessary: If the person is not breathing or has no pulse, begin CPR until medical help arrives.
Preventing Allergic Reactions
Avoiding Allergens
- Identify Allergens: Know and avoid allergens that trigger reactions.
- Read Labels: Read food and medication labels to avoid known allergens.
- Pet Care: If allergic to pet dander, maintain a safe distance and consider treatments to reduce symptoms.
Preventive Medication
- Antihistamines: Taking antihistamines before exposure to known allergens can help prevent symptoms.
- Immunotherapy: For severe allergies, immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be an option.
Action Plan
- Emergency Plan: Have a written action plan and share it with friends, family, and coworkers.
- Carry Epinephrine Auto-Injector: If you have a history of anaphylaxis, always carry an epinephrine auto-injector.
When to Consult a Doctor
Initial Evaluation
- Persistent Symptoms: If you experience persistent or frequent allergy symptoms, consult an allergist for a thorough evaluation.
Severe Reactions
- History of Anaphylaxis: If you’ve had an anaphylactic reaction, it’s crucial to follow up with a specialist to manage the condition and prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector.
Conclusion
Allergic reactions can be frightening, but with proper knowledge and an action plan, it’s possible to manage symptoms effectively. From identifying and preventing allergens to responding quickly in emergencies, being prepared can make all the difference. If you suspect allergies, consult a healthcare professional for guidance and develop a personalized management strategy.